You've got Bitcash!
AKA: A Paper Bitcoin Wallet!
Welcome to the Future, Bitcoin Moguls!
You're holding in your hands an elementally new kind of magic.
A Paper Bitcoin Wallet.
This isn't just a piece of paper, oh no! It's YOUR ticket to the thrilling roller coaster ride of Personal Wealth & Sovereignty!

Your paper wallet is like a super-secret vault. It has a public address (that's like the vault's location), which anyone can see. But the private key (that's the vault's secret combination) is sealed inside. It's like a treasure chest, waiting to be unlocked!
But here's the twist - this treasure chest is meant to stay locked. Primarily intended to help you "Stack Sats". Saving accounts are DEAD, save in Bitcoin instead!
However, you can physically trade it, sell it, gift it, all without breaking the seal. It's physical Bitcoin trading, with a dash of mystery... Bitcash!
Steps to Use the Wallet
-
To add Bitcoin: Go to your exchange app, select "Send BTC(Bitcoin)". All other 'cryptos' sent will result in loss of funds.
Coinbase, Bybit, Binance. - Scan the QR of your paper wallet's public address and confirm you are sending an irreversible transaction from the exchange to your paper wallet public address.
- Once the transaction is broadcast by your exchange, you'll be able to use our balance checker below or any block explorer website like the one linked below to scan your wallet's public address and check the new balance of any public address!
- If you eventually need the funds and want to send it back to an exchange,(or any other Bitcoin address) break the paper wallet's factory seal to reveal the private key.
- Using this website, you can sign and broadcast an irreversible transaction from your paper wallet to any other public address of choice.
- Double, and triple check you're sending to the correct public address, then tap the scan private key QR button, scan the private key of your opened paper wallet and tap the sign & send button.
- There will be a confirmation denoting the balance of the address you're sending to as a way to re-confirm you're sending to the right address, once the confirm button is tapped it will be broadcast via the blockstream.info API and you may check the updated balance in 10-30 seconds when the transaction has gone through.
You can check your balance here blockstream.info
Click Here to Scan Pubic Address QR with Camera @ blockstream.infoFrequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How secure is a paper Bitcoin wallet?
A: As long as the private key isn't revealed, a paper Bitcoin wallet is one of the most secure ways to store your Bitcoin. Just make sure to keep it in a secure place! Like a Fireproof Safe!
Q: Can I use the paper wallet more than once?
A: Yes, you can receive Bitcoin to the same address multiple times. However, once the seal is broken to reveal the private key, it's recommended to transfer all the funds and discard the wallet. Otherwise: ensure no one copies your private key while you're not paying attention. Which would result in loss of funds.
Q: How do I spend or transfer Bitcoin from a paper wallet?
A: Spending or transferring Bitcoin from a paper wallet involves importing or "sweeping" the private key into a software or hardware wallet. This process can vary depending on the wallet used, so follow the specific instructions provided by your chosen wallet provider. We offer a sign and send tx form below, all data is proccessed locally and the transaction hex is broadcast via blockstream.info to the bitcoin mainnet.
Q: What if I lose my paper wallet?
A: If a paper wallet is lost, the Bitcoin can't be retrieved. It's up to you to keep your paper wallet safe and secure! Maybe time to look into "Multi-Sig" Wallets.
Testimonials
"Woof! My human used to be all thumbs with Bitcoin, but this paper wallet changed everything. Now, he's not only a Bitcoin wizard but also has more time for belly rubs and fetch. Tail-waggingly good!"
-
Buddy the Dog, Chief Happiness Officer
"Meow! My owner's Bitcoin storage was a never-ending puzzle until she found these paper wallets. Now she's not only bitcoin-savvy but also more relaxed, giving me extra treats and cuddles. A purrfect solution!"
-
Whiskers the Cat, Feline Financial Advisor
"Tweet! Managing Bitcoin was a real bird-brain teaser for my human. But with these paper wallets, she's flying high with confidence. More time for chirps and treats. Feather-tastically fabulous!"
-
Charlie the Parrot, Avian Asset Analyst
Ready to start your Bitcoin adventure? Get your paper Bitcoin wallet today!
Creating and Signing a Bitcoin Transaction: A Comprehensive Guide
1. Understanding UTXOs (Unspent Transaction Outputs)
A UTXO represents the unspent funds that you control. Think of it like a $20 bill in your wallet. If you want to spend $10, you must use the entire $20 bill and receive $10 back as change.
2. Defining the Transaction Elements
- Private Key: Your secret key that proves ownership of the funds. It's like a PIN code for a bank account.
- Recipient's Address: The public address of the person you're sending funds to.
- Amount to Send: The specific amount you want to send to the recipient.
- Transaction Fee: A fee paid to miners for processing the transaction. It's like a postage stamp for mail.
- Change: The remaining funds that are sent back to an address you control.
3. Creating the Transaction
- Select UTXO: Choose the UTXO(s) that will be the input(s) for the transaction.
- Create Outputs: Define the outputs, including the recipient's address, amount to send, and change.
- Calculate Fee: Determine the transaction fee based on the size of the transaction and network conditions.
4. Signing the Transaction
- Prepare Data: Gather all the data that needs to be signed, including inputs, outputs, and other transaction details.
- Apply Signature: Use your private key to sign the data. This creates a digital signature that proves you authorized the transaction.
- Hashing: The transaction is hashed using a cryptographic algorithm, creating a unique fingerprint.
5. Broadcasting the Transaction
- Submit to Network: The signed transaction is sent to the Bitcoin network.
- Miner Verification: Miners verify the signature using your public key, check that the UTXOs haven't been spent, and confirm that all other transaction details are valid.
- Confirmation: Once verified, the transaction is added to a block and confirmed.
Conclusion
Creating and signing a Bitcoin transaction involves several critical steps and components. It's a secure and decentralized process that ensures only the owner of the funds can spend them, and that the transaction is valid and authorized.
- Always Protect Your Private Key: It's the key to your funds. Never share it and consider using secure signing practices.
- Understand Fees: Transaction fees can vary. Higher fees can lead to faster confirmations.
- Test Before Sending Large Amounts: Consider using a testnet to practice before sending significant amounts.
By understanding UTXOs, private keys, digital signatures, and transaction fees, you can appreciate the robust and elegant design of the Bitcoin protocol. Whether you're a developer or a user, this knowledge empowers you to use Bitcoin with confidence.

Bitcoin B: A stylized representation of the Bitcoin symbol. With the Quote: "You don't have to buy Bitcoin. You can just watch the price increase over time."

Green Bitcoin: A representation of warless, eco-friendly world brought about by Bitcoin mining.

Tree of Life: Symbolizing the interconnection of all life on Earth. Where two tango under the glow of our Milky Way

Space City: A futuristic portrayal of a city in outer space.

Fiat and Bitcoin: A comparison between traditional fiat currency and Bitcoin.

Ocean Metro: A creative depiction of a bustling futuristic metropolitan ocean port.

Bitcoin Portal: A gateway to the world of Bitcoin and cryptocurrency.

Bitcoin: An iconic representation of the Bitcoin Symbol.

Digital Sovereignty: A concept showcasing the autonomy in the digital world.
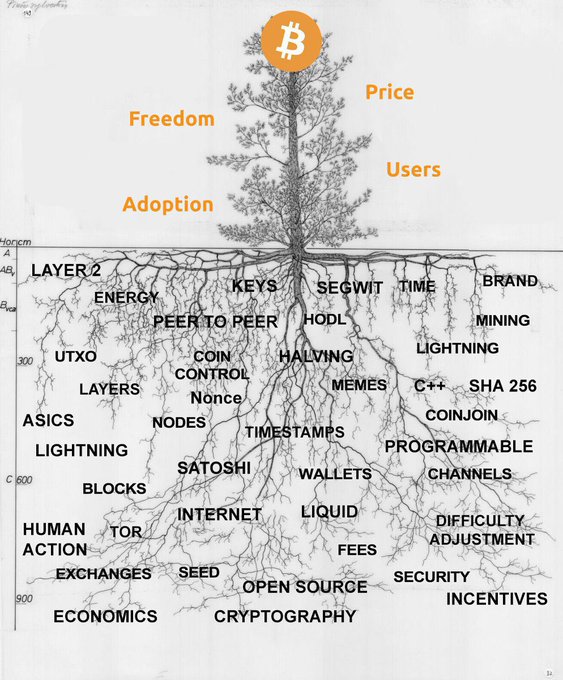
Bitcoin Roots: Illustrating the foundational principles and origins of Bitcoin.
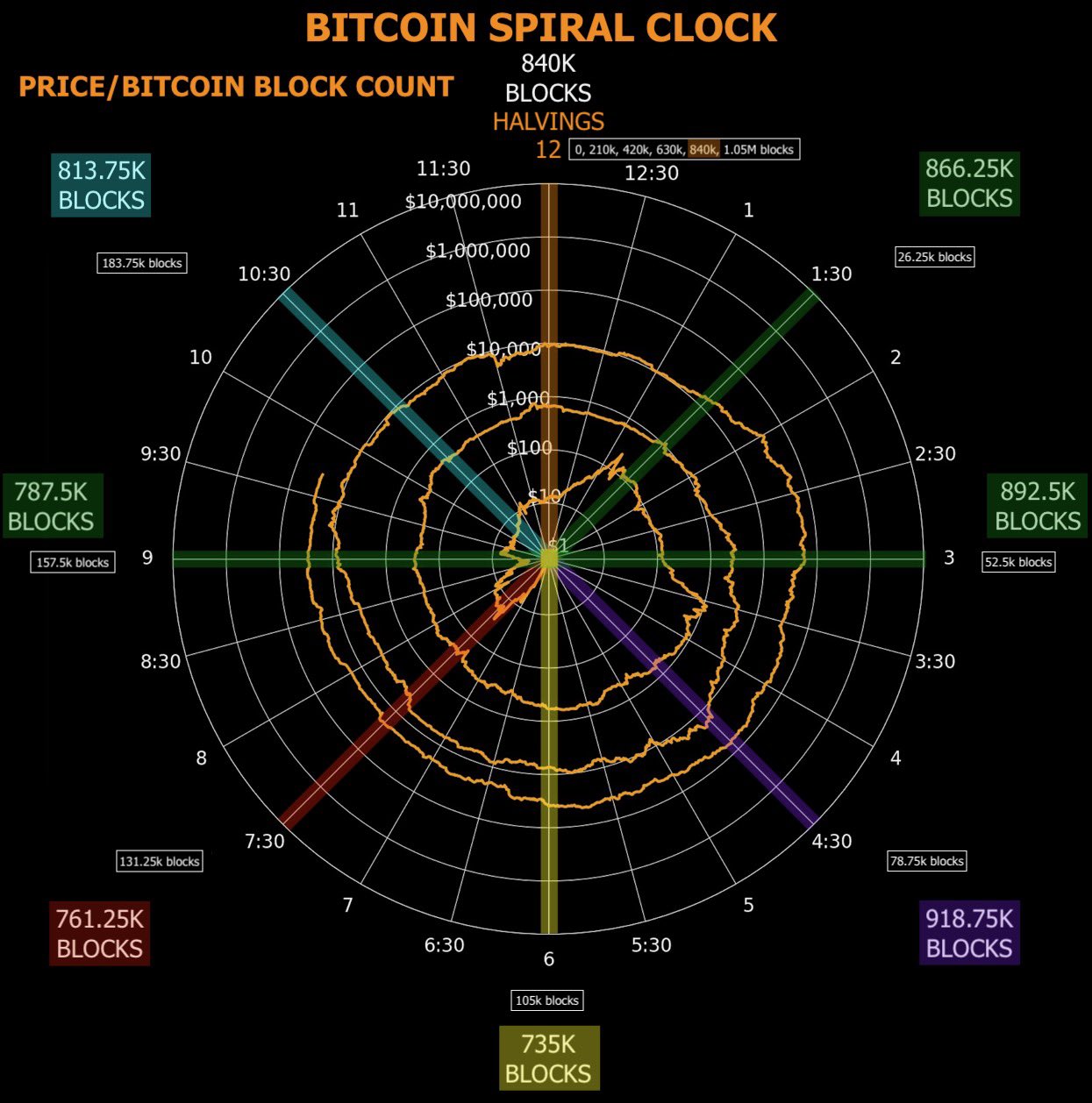
Bitcoin Spiral Clock: A visual metaphor for the increasing scarcity of Bitcoin's avalibility.
Components of the Bitcoin Spiral Clock
- Radial Component (Price): The radial component of the spiral represents the price of Bitcoin. As you move outward from the center of the spiral, the price increases. This can be seen as a metaphor for Bitcoin's potential price appreciation over time.
- Circumferential Component (Blocks Mined): Around the circle, the number of blocks mined is depicted. Since Bitcoin's inception, miners have been rewarded with newly created bitcoins (block rewards) for each block they mine. The circumferential component can represent the cumulative work and security of the network.
- Halving Events at 12 Noon: In the Bitcoin protocol, the block reward for miners is halved approximately every four years (or precisely every 210,000 blocks). This event is known as "halving," and it reduces the rate at which new bitcoins are created. By placing halving events at the 12 noon position on the clock, this visualization emphasizes the cyclical and predictable nature of Bitcoin's monetary policy.
Interpretation of the Bitcoin Spiral Clock
- Scarcity and Value Appreciation: By connecting the increase in price with the number of blocks mined, the spiral clock emphasizes Bitcoin's scarcity. The halving events reduce the supply of new bitcoins, leading to the idea that scarcity drives value appreciation.
- Time and Predictability: The clock metaphor underscores the time-bound nature of Bitcoin's monetary policy. The schedule for block rewards and halving events is coded into the protocol, making it transparent and predictable.
- A Journey Towards the Next Halving: The spiral can be seen as a journey towards the next halving event. As blocks are mined and the network progresses, the anticipation and speculation around each halving may influence price dynamics.
- Economic Cycle Visualization: The Bitcoin spiral clock can also be interpreted as a visual representation of Bitcoin's economic cycles, where each complete rotation of the clock leads to a new phase in Bitcoin's market dynamics.
Conclusion
The Bitcoin spiral clock is a rich and multifaceted metaphor that captures essential aspects of Bitcoin's unique value proposition. By integrating price, mining progress, and halving events into a single visual structure, it provides a snapshot of Bitcoin's complex interplay between scarcity, value, time, and economic cycles.
Bitcoin Halvening Countdown
What is Bitcoin Halvening?
Bitcoin halvening is an event where the reward for mining new blocks is halved, meaning miners receive 50% fewer bitcoins for verifying transactions. Halvening happens at intervals of 210,000 blocks, roughly every four years. This is significant because it can potentially increase the value of Bitcoin due to reduced supply.
Get involved in your Bitcoin revolution now!
or Support our webiste with a kind Donation.